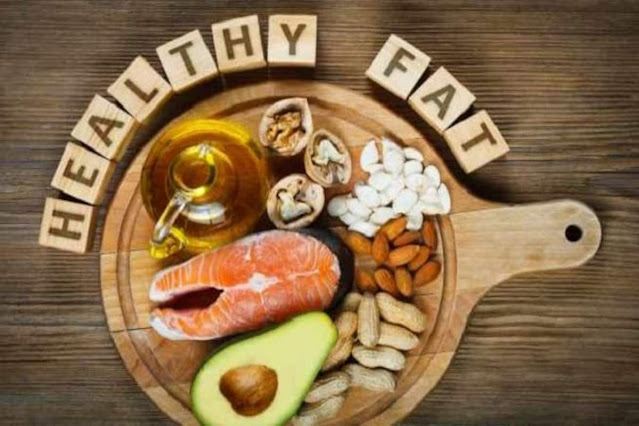
What is Healthy Fat?
Monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats are referred to as "good fats" since they are beneficial to your heart, cholesterol, and general health. These fats may help to reduce the risk of heart disease and stroke.
Monounsaturated fats - According to the US National Library of Medicine, monounsaturated fats help grow and maintain your cells and can help decrease your LDL cholesterol levels, lowering your risk of heart disease and stroke. According to the Mayo Clinic, they can be found in foods such as olive oil, almonds, and avocados.
Polyunsaturated fats - The two primary kinds of polyunsaturated fats are omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, which our systems cannot produce on their own but require for many critical activities, according to the American Heart Association (AHA). According to the US National Library of Medicine, omega-3 and fatty acids, in particular, are helpful for heart health, including lowering blood pressure and cholesterol and triglyceride levels. Omega-3 fatty acids may be found in a fish, nuts, seeds and etc.
Some best Healthy Fat Foods are here:-
1. Avocados - One medium avocado has around 21 grams of fat. These luscious green fat bombs are also high in fiber, with one avocado containing 9 grams. Eating one avocado every day is beneficial to your health. Avocados are also abundant in monounsaturated fat, fiber (9 grams for a medium avocado), and potassium, all of which have been linked to improved cardiovascular health.
2. Walnuts -
Walnuts are an excellent source of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, with 21 grams of fat in a 1-oz meal. They also include high levels of the minerals manganese and copper. (They also happen to be tasty, so they deserve to be on this list even more.)
3. Almonds -
Nuts in general are high in fat. While it's difficult to go wrong with any type, we love almonds since they offer 15 grams of fat in a 1-oz. serving (approximately 22 nuts) and are high in vitamin E.
4. Nut butter -
The scoop: A nut or seed butter may be an even tastier way to receive all the fatty benefits of nuts. Try almond, cashew, or sunflower seed butter instead of peanut butter for a plant-based dose of creamy richness (plus fiber and protein). Two tablespoons of both peanut butter and sunflower seed butter, for example, have 16 grams of fat.
5. Dark chocolate -
Dark chocolate is high in antioxidants and minerals and has less sugar than milk chocolate. Dark chocolate may help cut the risk of heart disease, reduce inflammation and insulin resistance, and boost cognitive function, according to some study.
6. Chia seeds - The scoop: Their cult following is well-deserved: These tiny but powerful seeds are high in fiber, protein, vital minerals, and, of course, fat—6 grams per 2 tablespoons, with enough of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids.
Thankyou for visiting



Comments